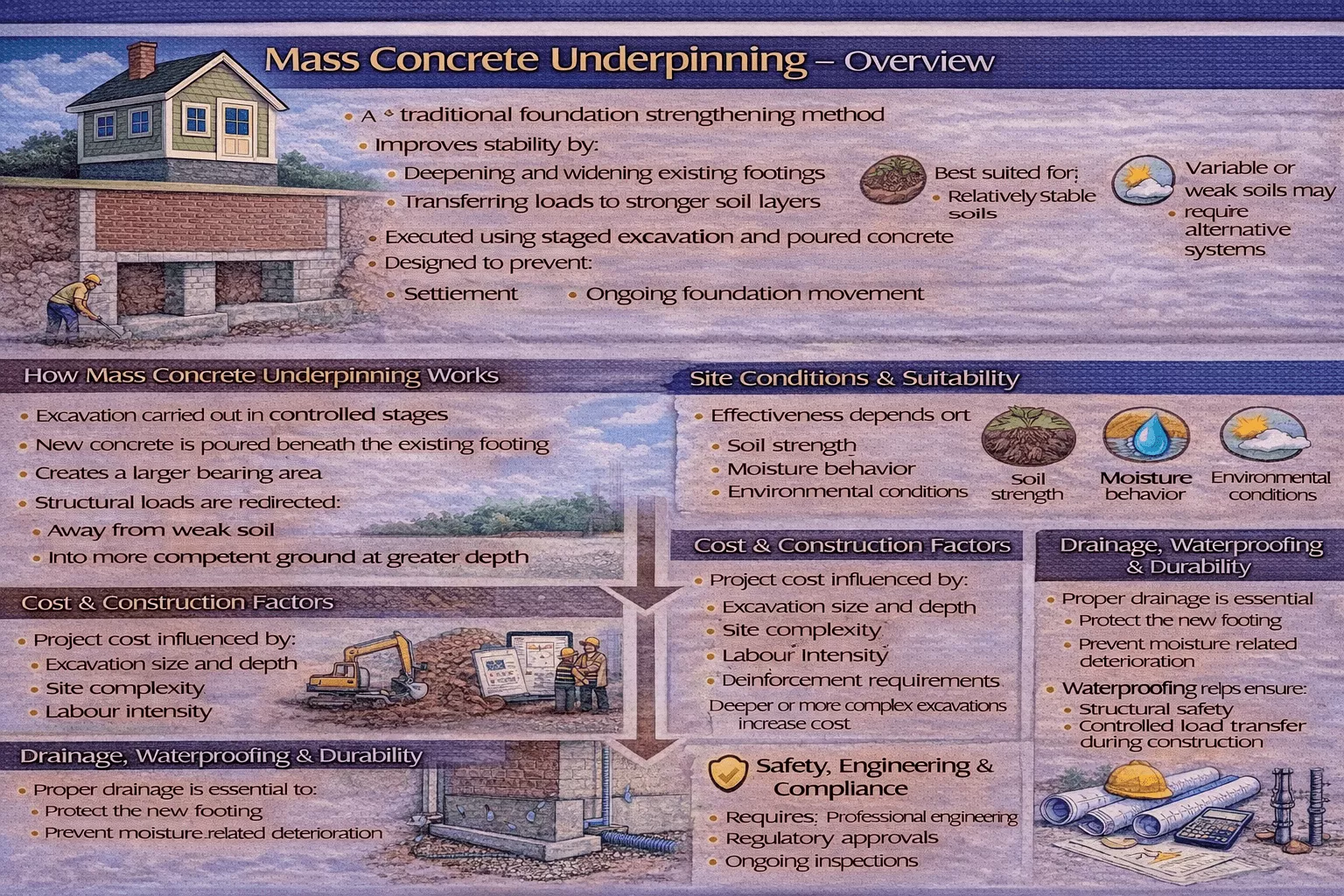
Chemical and jet grouting strengthen weak or voided soils, control groundwater, and provide stable support for basement underpinning without the disruption of excavation-based repairs. Low-viscosity chemical grouts permeate granular soils, bind particles, and form dense, cohesive masses that increase bearing capacity while reducing movement risks around existing structures. The effectiveness of the method depends on selecting the correct grout type, such as acrylamide gels, sodium silicate systems, polyurethane foams, or epoxies, based on soil permeability, groundwater conditions, and project requirements. Reliable outcomes require detailed site assessment, proper drilling access, controlled injection sequencing, and strict monitoring to ensure uniform penetration and long-term stability.
Comparing chemical grouting with traditional soil improvement methods remains essential for addressing geotechnical challenges, environmental considerations, and project-specific needs. Incorrect application risks structural cracking, water ingress, corrosion, and costly repairs, making proper training and adherence to safety and regulatory standards critical. When designed and executed properly, chemical and jet grouting deliver durable soil stabilization, reduced permeability, and safe, precise underpinning in confined or sensitive basement environments.
How does chemical grouting strengthen weak ground?
Chemical grouting strengthens weak ground by permeating the soil structure with low-viscosity chemical substances. This method involves injecting grout that infiltrates the spaces between granular soil particles or narrow cracks. Once injected, the chemical grout binds these particles together, creating a denser, more cohesive structure capable of supporting higher loads and resisting deformation.
This process significantly improves the soil strength and stability, thereby increasing the soil’s bearing capacity, which is essential for stable deep foundations. Furthermore, chemical grouting is used to control water flow and provides superior sealing capabilities, and because the application is vibration-free, it minimizes the risk of damage to nearby structures during the enhancement process.

What grout formulas give the best soil improvement?
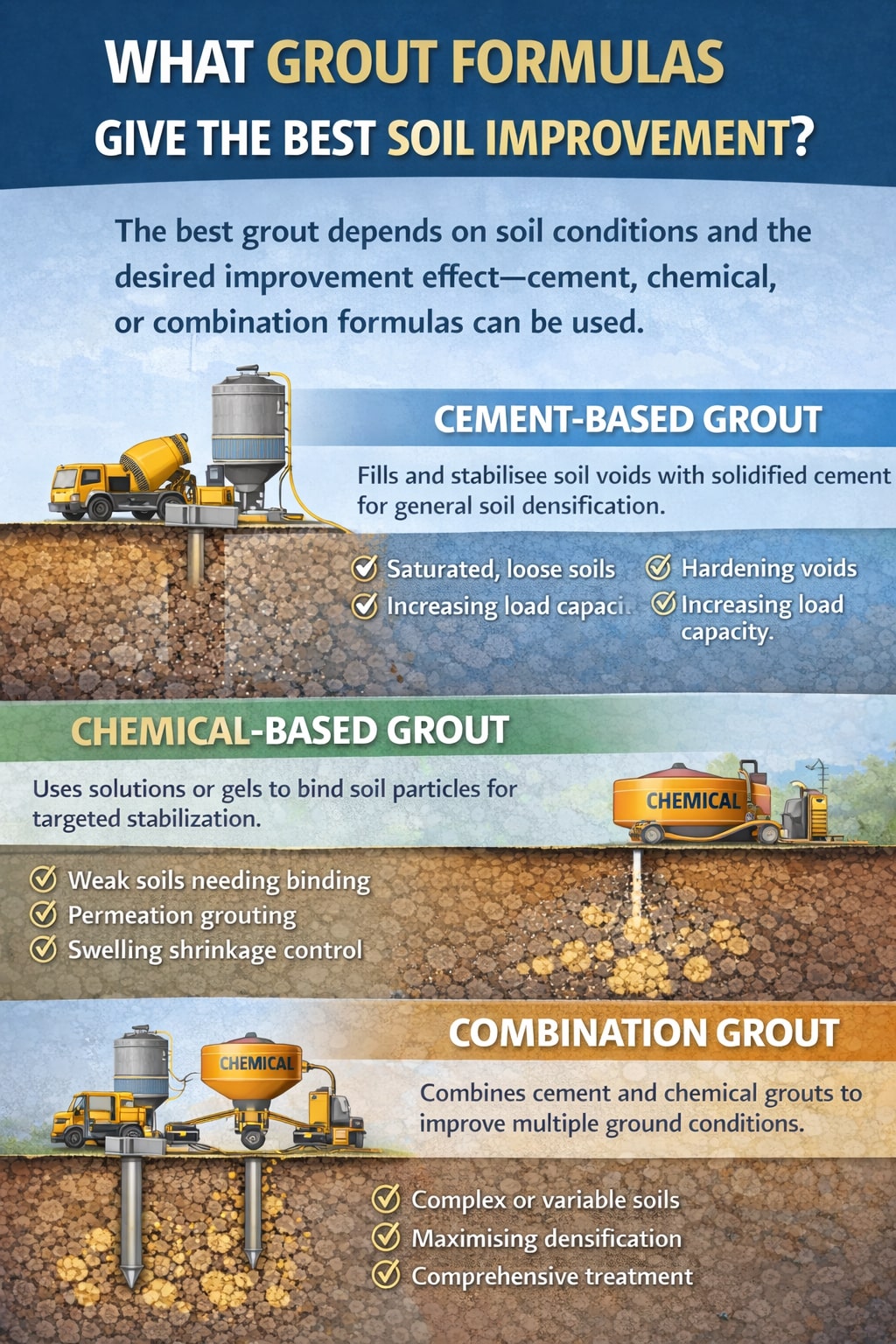
The grout formulas that give the best soil improvement are typically chemical grouts, whose selection depends heavily on the soil permeability, groundwater conditions, and required strength characteristics of the site. Grouting is an essential ground improvement technique that involves injecting these formulas to fill voids, compact soil, enhance stability, and mitigate settlement.
These chemical grouting systems, utilized for improving soil strength and specific site conditions, include the following specialized formulas:
- Acrylamide and Acrylic Gels: Known for their ultra-low viscosity and deep penetration, these gels are ideal for stabilizing fine soils.
- Sodium Silicate Grouts (Silicate-based): These formulas create a dense, glass-like gel that effectively stabilizes sandy or loose soils. Silicate-based grouts also work well in coarse soils with high permeability.
- Polyurethane Grouts: Ideal for sealing active leaks or filling voids because they expand significantly upon reaction with water.
- Gel-forming Chemicals: Generally better suited for controlling water infiltration in fractured rock or very permeable formations.
- Epoxy Grouts: While providing high strength and chemical resistance, these are typically used for specialized structural applications rather than broad mass soil stabilization.
How does chemical grouting manage groundwater flow?
Chemical grouting manages groundwater flow by transforming granular soils into effective, long-lasting water barriers with reduced permeability. This process involves injecting a low-viscosity, non-particulate chemical grout under pressure, often through sleeve port pipes in pre-drilled holes or directly through pipe joints and cracks, into the surrounding soil.
For managing sewer or pipeline leaks, a packer is typically inflated over the leak, and the grout is injected, flowing through the joints and into the soil outside the pipe. The grout permeates the voids in the granular material, where it gels with the soil and hardens rapidly, sometimes in under a minute. This curing process creates a waterproof mass—often described as a sandstone-like mass—that cannot be pushed back into the system. The resulting grouted soil exhibits increased strength, stiffness, and significantly reduced permeability, forming a durable water barrier.

How is a chemical grouting plan designed for reliable outcomes?

A chemical grouting plan for reliable outcomes is designed by first establishing comprehensive site knowledge and then executing a precise, multi-stage process. This approach ensures precise, long-lasting, and cost-effective solutions.
The reliable design process includes the following steps:
- Detailed Site Inspection and Material Selection: The design begins with a detailed inspection of the affected area to identify all cracks, voids, and weak soil zones where the grout will be injected. This crucial assessment dictates the best grout type (such as specialized polyurethane or acrylate, informed by advanced industry knowledge) and the optimal injection points.
- Site Preparation and Access Drilling: Before injection, the site must be thoroughly cleaned, loose debris removed, and the surface dried to ensure the grout bonds well. To allow the grout to reach deep cracks or underground spaces, small holes may need to be drilled into the concrete or soil. This preparation stage, along with essential safety preparations like readying equipment and wearing protective gear, controls the grout flow and prevents waste or damage.
The reliability of the outcome is achieved through the operational mechanism: when the chemical grout is subsequently injected under pressure, it permeates the spaces between the soil or rock particles. This meticulous approach, often utilizing grid-pattern injections to create subterranean curtains, forms a comprehensive, waterproof mass that effectively halts water migration, stabilizes the surrounding area, and reinforces the integrity of existing structures.
Should chemical grouting replace excavation-based repairs?
Whether chemical grouting should replace excavation-based repairs depends on the specific application, but it offers significant advantages as a non-invasive, cost-effective solution compared to extensive excavation or full replacement. Chemical grout provides a fast and reliable way to stabilize soil, seal cracks, and protect a structure from issues like sinking slabs, early sinkhole signs, or moisture intrusion without major disruption.
The primary benefits demonstrating why chemical grouting is a superior alternative in many situations include:
- It is non-invasive and cost-effective, eliminating the need for extensive excavation or full structural replacement.
- It can be easily performed in areas where access and space are limited.
- It requires no structural connection to the foundation being underpinned, making it an ideal application for providing excavation support or underpinning existing, adjacent structures.
- The technique can typically be accomplished without disrupting normal facility operations.

Why compare chemical grouting with other soil improvement methods?
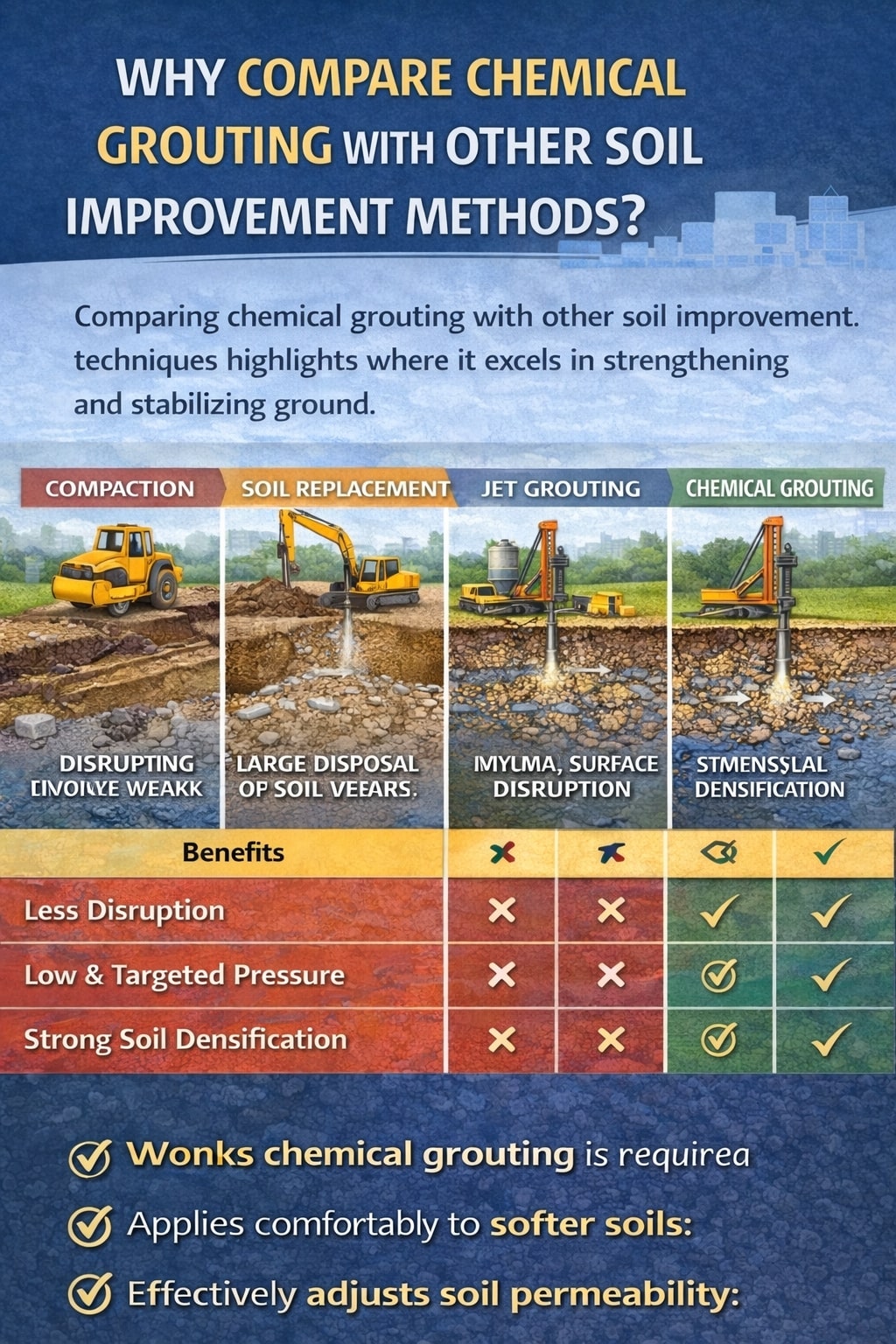
The reasons for comparing chemical grouting (a technique utilizing chemical stabilizers) with other soil improvement methods are rooted in the critical need for effective and safe geotechnical solutions for designing structures in weak soil. Comparing these techniques is essential for making informed decisions based on technical efficacy, project needs, and environmental impact.
Key reasons for the necessity of this comparison include:
- Evaluating Effectiveness Against Traditional Methods: Chemical grouting provides an excellent alternative to traditional methods, requiring comparison to summarise its applicability conditions and ensure successful projects, which often combine multiple techniques to address soil improvement needs comprehensively.
- Addressing Specific Geotechnical Challenges: Grouting is particularly effective in controlling groundwater flow, a challenge that may not be as directly addressed by traditional stabilization methods, highlighting a unique technical advantage that must be weighed during method selection.
- Mitigating Environmental and Safety Concerns: Comparison is necessary to develop more environmentally friendly and safe methods, as chemical stabilizers still lack a proper understanding regarding their use, handling, application, and long-term effect on the environment, which is a major concern.
- Informing Project Selection Criteria: The selection among soil improvement methods requires careful consideration of project-specific factors, including soil conditions, loading requirements, environmental constraints, and economic considerations.
What risks arise when chemical grouting is applied incorrectly?
The risks that arise when chemical grouting is applied incorrectly include various forms of structural damage, cosmetic failure, and corrosion, often requiring costly subsequent repairs.
Specific negative effects associated with incorrect chemical grouting application include:
- Developing long-lasting structural cracks that compromise the overall strength of the building.
- Causing the joints to crack and crumble, or leading to water ingress beneath surfaces like floor tiles, especially if movement and moisture are introduced before the material has fully set.
- Rusted hinges and moisture seepage due to incorrect application methods (such as pumping slurry instead of hand troweling), which can trap moisture within surrounding materials like door frames.
- The necessity of costly and extensive repairs to fix the damage resulting from the initial application failure.

Why compare chemical grouting with other soil improvement methods?

The reasons for comparing chemical grouting (a technique utilizing chemical stabilizers) with other soil improvement methods are rooted in the critical need for effective and safe geotechnical solutions for designing structures in weak soil. Comparing these techniques is essential for making informed decisions based on technical efficacy, project needs, and environmental impact.
Key reasons for the necessity of this comparison include:
- Evaluating Effectiveness Against Traditional Methods: Chemical grouting provides an excellent alternative to traditional methods, requiring comparison to summarise its applicability conditions and ensure successful projects, which often combine multiple techniques to address soil improvement needs comprehensively.
- Addressing Specific Geotechnical Challenges: Grouting is particularly effective in controlling groundwater flow, a challenge that may not be as directly addressed by traditional stabilization methods, highlighting a unique technical advantage that must be weighed during method selection.
- Mitigating Environmental and Safety Concerns: Comparison is necessary to develop more environmentally friendly and safe methods, as chemical stabilizers still lack a proper understanding regarding their use, handling, application, and long-term effect on the environment, which is a major concern.
- Informing Project Selection Criteria: The selection among soil improvement methods requires careful consideration of project-specific factors, including soil conditions, loading requirements, environmental constraints, and economic considerations.
Why do rules and safety standards matter in chemical grouting?
Rules and safety standards matter significantly in chemical grouting because they ensure the legal compliance of the operation, protect worker and public safety, maintain structural integrity, and guarantee the long-term effectiveness of the soil stabilization or repair.
The importance of following these regulations and standards can be categorized by the following core necessities:
- Ensuring Legal and Environmental Compliance: Adherence to established rules is critical for responsible operation. This includes following specific OSHA regulations for chemical handling and workplace safety, plus complying with environmental laws designed to prevent chemical spills into nearby soil or water. Following recognized standards also requires using grouting tools and materials that are certified for construction use, reducing the risks of accidents or long-term problems.
- Protecting Worker Safety and Structural Integrity: Following defined safety standards is essential for mitigating the serious challenges posed by unstable or shifting soils at construction sites, such as tunnels and trenches. Chemical grouting, when performed under proper guidelines, reliably solidifies the soil, minimizes dangerous shifts, and creates a protective layer that stops groundwater or rain from infiltrating the work zone, helping maintain a stable and secure environment for ongoing operations.
- Guaranteeing Quality Control and Effectiveness: The ultimate success of a grouting program depends on careful planning and quality control established by industry standards. This includes pre-injection soil testing to determine the optimal grout type, pressure, and flow rate. During the application, standards dictate that pressure and volume data are closely monitored to ensure complete coverage of the area without fracturing the surrounding soil.

Why does chemical grouting require ongoing maintenance checks?
Chemical grouting requires ongoing maintenance checks because routine inspection and a commitment to long-term care are essential for maintaining the performance, longevity, and resilience of the grouted structures and seals, particularly in concrete constructions.
Continuing to check waterproofing areas on a regular basis helps identify problems early, such as tiny leaks, cracks, and stains, which require immediate remedial steps. This proactive approach decreases the risk of a developing issue and prevents significant subsequent damage, such as concrete cancer, thereby ensuring the continuing effectiveness of the chemical grout in addressing system leaks without escalating into the need for more intensive structural rehabilitation methods.
Why is chemical grouting assessed for long-term cost efficiency?
Chemical grouting is assessed for long-term cost efficiency because it offers significant advantages in durability, application method, and material usage:
- When properly applied in appropriate conditions, it serves as a long-lasting and effective solution that prevents structural damage by stopping infiltration caused by leaks and failing joints in otherwise sound pipes, making it a critical component of wastewater maintenance and rehabilitation programs.
- The process involves minimal invasiveness, which negates the need for extensive and costly excavations commonly required for applications like foundation repairs, tunnel construction, and soil stabilization.
- It is a cheaper way to accomplish waterproofing and soil stabilization because it requires the use of less material and significantly reduces the direct costs associated with excavation.
How do application errors impact chemical grouting performance?
The impact of application errors on chemical grouting performance is severe, primarily by undermining the strategic approach necessary for successful structural reinforcement and sealing, which ultimately compromises the material’s effectiveness and long-term durability.
Grout injection is a challenging step that requires a strategic approach where technique and alignment play pivotal roles. Failure to execute these steps correctly affects the workability, stability, injectability, consistency, and rheology of the material, leading to a diminished ability to manage water leakage and secure the integrity of the structure.
Application errors directly impede the intended functions of the grout, leading to the following performance failures:
- Inability to adequately fill the cavity, preventing effective sealing of cracks or voids.
- Failure to ensure the secure anchorage of the grout within the structure, reduces its mechanical strength and long-term stability.
- A compromised defence against rust and other environmental factors, jeopardizes the overall safety and serviceability of the structure.
If not applied correctly, application errors can negate the benefits of suitable grout materials (such as WPU or OPU slurries, which are capable of sealing water leakage) and may lead to catastrophic structural failures, particularly in cases like prestressed concrete structures where the deterioration is non-inspectable.
How do regulations influence chemical grouting use?
Regulations influence chemical grouting use by establishing mandatory safety protocols, strict environmental protection requirements, and necessary post-application verification standards, ensuring the work is conducted legally, ethically, and effectively.
Specific regulatory requirements that guide chemical grout injection work include:
- Workplace Safety and Chemical Handling: These rules, which often include OSHA regulations, dictate safe procedures for chemical handling and workplace safety, specify guidelines for using injectables like polyurethane, and require that grouting tools and materials must be certified for construction use. Following these standards reduces the risk of accidents and long-term problems.
- Environmental Protection Compliance: Environmental laws mandate specific protocols to prevent chemical spills into nearby soil or water. Compliance is essential, particularly in jurisdictions requiring protection protocols when working near water sources, ensuring adherence to legal and ethical construction practices.
- Verification of Engineering Performance: Regulations require post-grouting verification methods to confirm that the foundation meets the required engineering performance standards. These verification steps include borehole sampling, core extraction, and permeability testing to confirm the extent and uniformity of the improvement achieved by the chemical grouting.